tg-me.com/Machine_learn/3501
Last Update:
Executable Code Actions Elicit Better LLM Agents
1 Feb 2024 · Xingyao Wang, Yangyi Chen, Lifan Yuan, Yizhe Zhang, Yunzhu Li, Hao Peng, Heng Ji
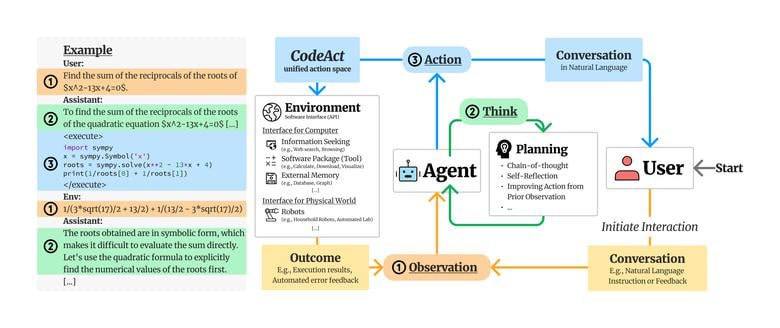
Large Language Model (LLM) agents, capable of performing a broad range of actions, such as invoking tools and controlling robots, show great potential in tackling real-world challenges. LLM agents are typically prompted to produce actions by generating #JSON or text in a pre-defined format, which is usually limited by constrained action space (e.g., the scope of pre-defined tools) and restricted flexibility (e.g., inability to compose multiple tools). This work proposes to use executable Python code to consolidate LLM agents' actions into a unified action space (CodeAct). Integrated with a Python interpreter, CodeAct can execute code actions and dynamically revise prior actions or emit new actions upon new observations through multi-turn interactions. Our extensive analysis of 17 LLMs on API-Bank and a newly curated benchmark shows that CodeAct outperforms widely used alternatives (up to 20% higher success rate). The encouraging performance of CodeAct motivates us to build an open-source #LLM agent that interacts with environments by executing interpretable code and collaborates with users using natural language. To this end, we collect an instruction-tuning dataset CodeActInstruct that consists of 7k multi-turn interactions using CodeAct. We show that it can be used with existing data to improve models in agent-oriented tasks without compromising their general capability. CodeActAgent, finetuned from Llama2 and Mistral, is integrated with #Python interpreter and uniquely tailored to perform sophisticated tasks (e.g., model training) using existing libraries and autonomously self-debug.
Paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2402.01030v4.pdf
Codes:
https://github.com/epfllm/megatron-llm
https://github.com/xingyaoww/code-act
Datasets: MMLU - GSM8K - HumanEval - MATH
@Machine_learn
BY Machine learning books and papers
Share with your friend now:
tg-me.com/Machine_learn/3501
